After determining the personalized treatment plan, ovarian stimulation is commenced on the second or third day of menstruation. For this purpose daily injections (Gonal F or Puregon or Menopur or Menogon or Fostimon or Merional) are prescribed and used. Since the vast majority of these medications are in the pen-form and very patient friendly to use, our patients, near exclusively self-administer these drugs following initial demo.
Drugs are used on a daily basis to stimulate the ovaries, the dose of which is assigned based on the patient’s ovarian reserve status, body mass index (calculated by the weight and height of the patient) and her previous response, if available. Ovarian reserve may not necessarily be correlated with chronological female age. To assess ovarian reserve, we mainly use the so-called bilateral antral follicle count, which is the number of 2-10 mm sized follicles in both ovaries. Occasionally, we additionally use the blood test, anti-mullerian hormone (AMH) for this purpose.
Protocols used in IVF to stimulate the ovaries;
- Long Protocol; Luteal long lucrin protocol, with or without oral contraceptive pill,
- Short Protocol; GnRH Antagonist protocol
- Micro dose flare up,
- Mini IVF Protocol,
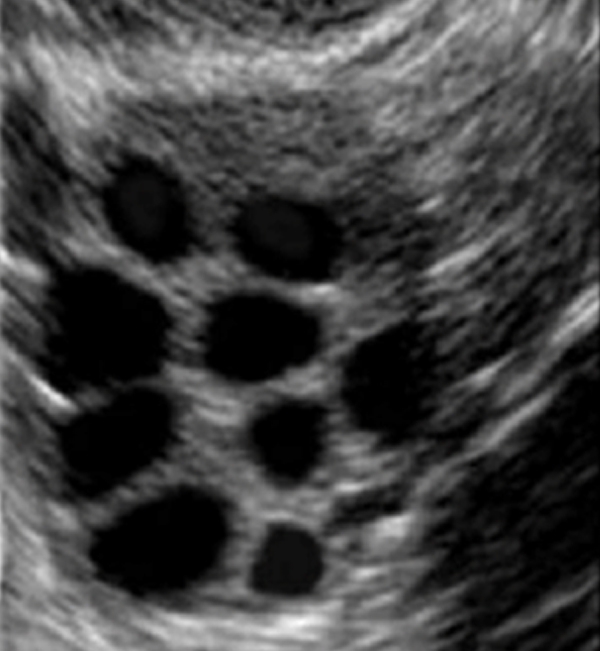
Follicular growth is monitored by frequently performed trans-vaginal ultrasonography and blood estradiol (E2) levels, all done at our IVF center. There is no need for fastening before such testing. The daily dosage of drugs used to stimulate the ovaries (Gonal-F or Puregon or Menopur or Menogon or Fostimon or Merional) is adjusted based on the results of trans-vaginal ultrasonography and E2. Our nurses give a call, usually in the afternoon, for such dose assignments. The patients only need to spend 15-20 minutes at our center for trans-vaginal ultrasonography and E2.
Final shut injection (Ovitrel/Triptorelin) is performed when follicles reach 17-18 mm in diameter as assessed by trans-vaginal ultrasonography. Oocyte pickup procedure (OPU) is performed under light general anesthesia 34-36 hours later. The type of final shut injection is determined based on the ovarian response and will be decided by your physician.
Treatment may be cancelled before final shut injection in around 10-15% cycles; the main reasons for cancellation are insufficient ovarian response due to diminished ovarian reserve and discordant follicular growth.