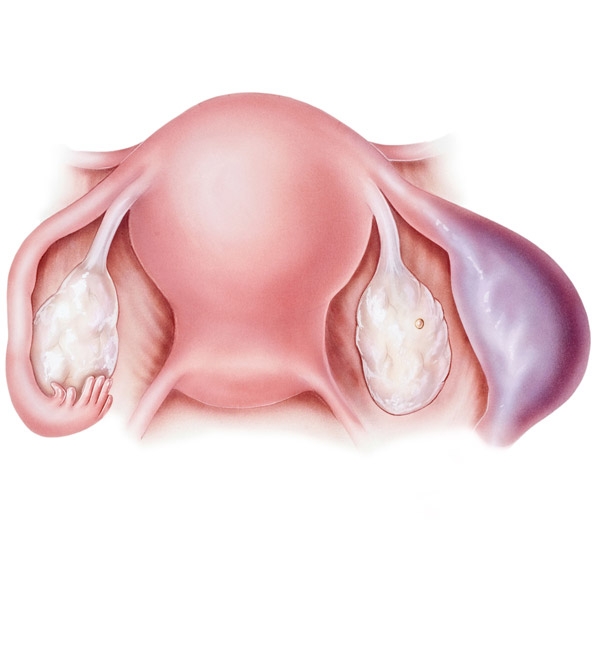
Hydrosalpinx refers to the complete obstruction of the end of the tube and accumulation of fluid inside the tube. The main reasons for hydrosalpinx are prior sexually transmitted disease, adhesions due to prior surgery, endometriosis or appendicitis.
The gold standard for the diagnosis of hydrosalpinx is hysterosalpingography (HSG; X-ray film of the uterus and tubes with contrast medium). In some cases, the diagnosis might also be made with trans-vaginal ultrasonography.
The presence of hydrosalpinx is detrimental to IVF outcome, since i) it decreases pregnancy/implantation rates; ii) it may increase miscarriage rates, and iii) it may increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy. Although embryos are classically transferred inside the cavity during embryo transfer, embryos might move into the tube and might be blocked to re-enter to the cavity due to adhesions inside the tube in patients with hydrosalpinx. Hence, the risk of ectopic pregnancy is increased. To conclude with, the live birth rates are decreased by 30-35% with the presence of hydrosalpinx.
With all these information, prior removal of the tube(s) (salpingectomy) is recommended in patients suffering from hydrosalpinx. This operation is performed via laparoscopy. However, in some cases, severe adhesions might be encountered making such surgery very difficult. In such cases, tubal blockage at the connection of the tube with uterus might be performed yielding similar success rates following surgery. Very rarely, even such blockage might prove to be very difficult due to severe adhesions; in such cases, coagulation-burning of the entrance points of the tubes at hysteroscopy (endoscopic assessment of the uterus) might be performed as the last treatment option.